Mitochondrial dysregulation in the myocardium of a model of Maturity Onset diabetes in the Young (MODY) and impact of diet Case Study Solution
Etiological Factors of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diabetes
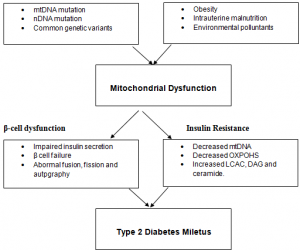
In early 1990s, the identification of a specific type of mutation in mitochondrial DNA which is related to the inherited form of diabetes from the mother to her offspring. (Soo Heon Kwak, 2010)The oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria is the main energy source in cardiac muscle. (Jia-Ying Yang, 2009)Therefore, the etiological factors affecting the functions of mitochondria in diabetes are described as: (Soo Heon Kwak, 2010)
Genetic Factors Environmental factors
Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in Insulin Resistance:
The metabolism of lipid and glucose are mainly mitochondria dependent for generation of energy in the cells. Therefore, the inefficiency in the oxidation of nutrients, the oxygen consumption or ATP production ratio is considered low which leads in the increased superoxide anions production. Species formation of reactive oxygenis expected to have the consequences of maladaptationincreasing the mutagenesis rate and stimulation of pro-inflammatory processes.
Additionally, with the species formation of reactive oxygen reduced biogenesis of mitochondria, aging and genetic factors contribute in the dysfunction of mitochondria. Such factors also play their part in resistance of insulin in both target issues non-classic and classic ones. Resistance of insulin has emanated from the dysfunction of mitochondria contributing to abnormalities of cardiovascular and metabolic activities and consequent rise in cardiovascular diseases. In insulin, its metabolic actions are responsible for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis through glucose uptake promotion in skeletal muscle and suppressed production of glucose in liver.
Regulation of metabolic actions is mainly dependent on mitochondria which is essential in the homeostasis of energy through nutrients metabolizing and production of ATP and heat. Differencein the expenditure and energy uptake results in the dysfunction of mitochondria which is characterized through anenergy/ATP production ratio to respiration. (Jeong-a Kim, 2008)
Molecules Linking Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Insulin Resistance
Fat derivative like ceramides, DAG –diacylglycerol, LCAC – long chain acyl-CoA mediate dysfunction of mitochondria for the resistance of insulin. Decrease in the fatty acid oxidation of mitochondria give rise to cytosolic long chain acyl-CoAwhich is a potent hexokinase and glycogen synthase inhibitor leading in the resistance of insulin. Additionally, the diversion of increased long chain acyl-CoA to ceramides and diacylglycerol as they are known on the basis of their capability to increase the resistance of insulin.
In past literature, an obese rat model i.e. prone to diabetes showed significant decrease in AMPK in comparison to the normal controls. AMPK – an energy gauge of cell which is responsible to sense the ratio of ATP/AMP. The activation of this energy gauge leads to acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibition resulting in the decrease in synthesis of fatty acid in liver with the increase in oxidation of fatty acid in the muscle. Remarkably, the expression of PGC -1α can be increased by AMPK and the subsequent pathway of biogenesis of mitochondria. In contradiction with obesity, restriction of calorie and physical activity increases the level of AMPK and PGC -1α leads to increased sensitivity of insulin.
In recent times, MFN -2 (mitofusion) protein is considered to show the mediation of the PGC -1α role on the biogenesis of mitochondria. MFN -2 (mitofusion) protein is a membrane protein of mitochondria involving in the membrane fusion of mitochondria and its metabolic activities. (Jia-Ying Yang, 2009)
Aim of Study:
In this study, the rat model will be used for the determining the functioning of the gene GENA348. A high fat diet will be provided to the rat among different groups that are to be studied and analyzed. Though, the key objectives to the study are:
- The expression of gene of these rat groups are to be investigated using technique of western blotting as it is particularly designed for the study of protein molecules and their function of the mitofusion (MFN) protein.
- The fractions of mitochondria are to determine through the process of mass spectrometry resulting in the changes of protein structure altering the functions of protein through oxidation and dysfunction of mitochondria.
- Use of mass spectrophotometry assay to evaluate the enzymatic activity
This is just a sample partical work. Please place the order on the website to get your own originally done case solution.
How We Work?
Just email us your case materials and instructions to order@thecasesolutions.com and confirm your order by making the payment here