Material Properties
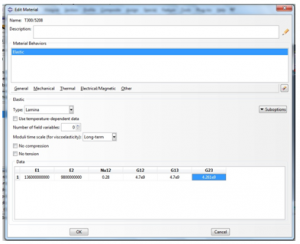
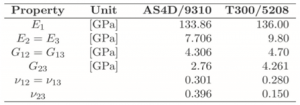
The material used in this following exercise for the lamination is carbon/epoxy T 300/5208. According to the brief document (see in Table-1 and Table-2 in Appendix) the lamination properties of this particular material is,
These properties can be seen below,
Figure 1 lamina settings
4 Geometry
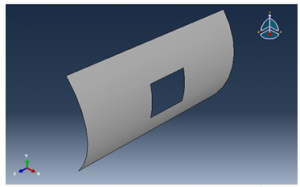
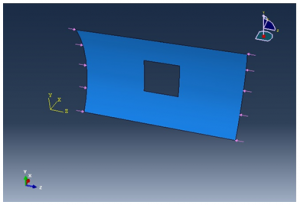
The geometry of the cylindrical panel depends upon the student ID and since the last 5 numbers of the ID is 93670 S1 is taken as 9, S2 = 36 and S3 is taken as 90, the radius of the circle is calculated to be 136 and the length of the panel is calculated to be 270, all the calculations are shown in section 6.
Figure 2 Design
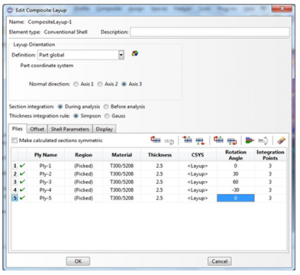
The lamination is also done using the angles in the brief document, the below picture shows the work,
Figure 3 layup
Figure 4 The lamination Layup
5 Boundary Conditions
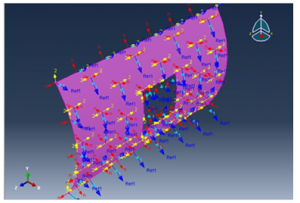
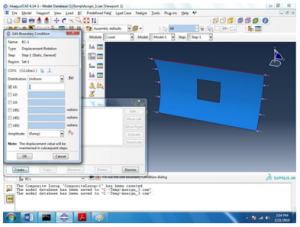
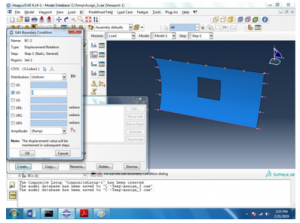
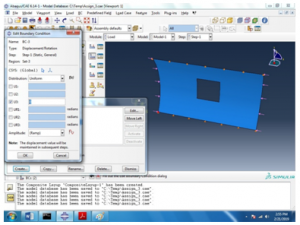
The boundary conditions are taken to be simple that is E 1, E 2 and E 3 all equal to 0. That can be seen below,
Figure 5 Boundary condition 1
Figure 6 Boundary condition 2
Figure 7 Boundary condition 3
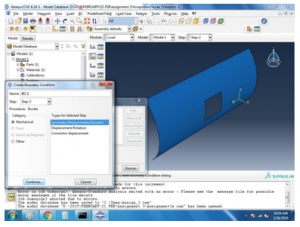
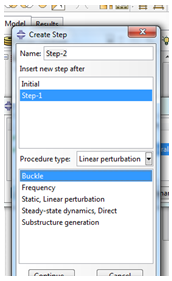
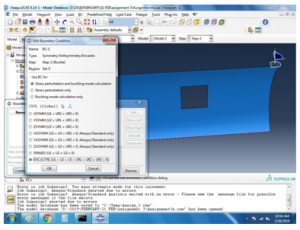
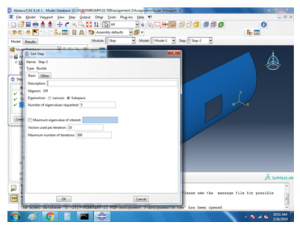
For the buckling analysis the following boundary conditions are used,
Figure 8 Buckling analysis
Figure 9 Buckle Selection
Figure 10 Boundary setting
Figure 11 variables for buckle analysis selection
6 Loads
The loads applied to the sides of the panels is selected to be 0.15 N/mm as told.
Figure 12 Load at 0.15 N/mm
7 Detailed Calculations
Calculations of geometry:
Given: S1 = 9, S2 = 36, S3 = 70
In XY-plane:
In Z-direction:
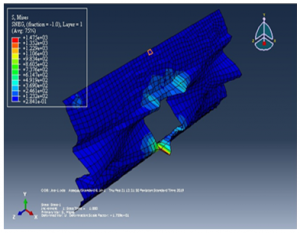
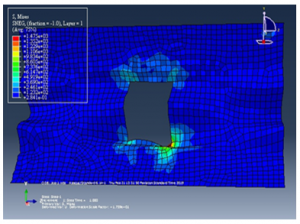
For this shell model, the result of stress as shown in the following:
Figure 13 stress after pressure applied
Figure 14 stress after pressure applied another angle
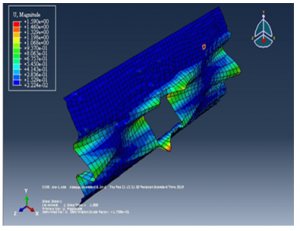
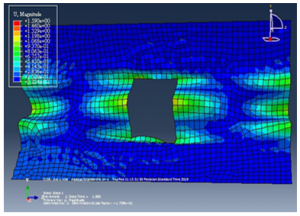
The result of displacement as shown in the following:
Figure 15 displacement after pressure applied
Figure 16 displacement after pressure applied another angle
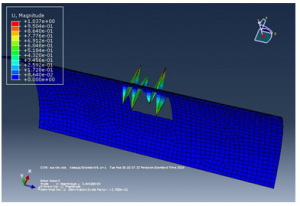
Buckle analysis Solution:
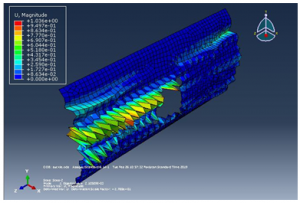
Figure 17 Buckle analysis solution
Figure 18 Another view of the result
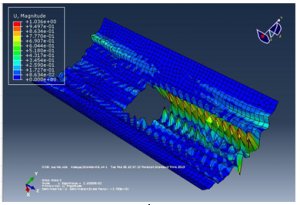
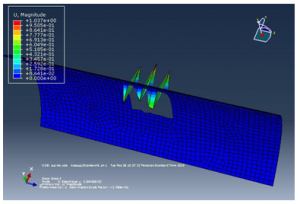
Figure 19 Lamina 2 result
Figure 20 Lamina 3 result
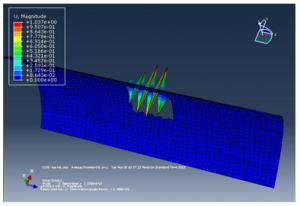
Figure 21 lamina 4 result
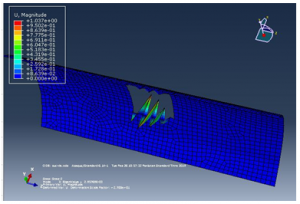
Figure 22 lamina 1 and 5 result
8 Conclusion
The results above are, using the geometry of own design, the maximum stress at the panel is found to be 1470 N/mm^2. The maximum displacement at the panel is found to be 1.59 mm, figure 1 shows the material properties of the designed structureand basics characteristics of the designed structure, the design structure is analyzed with extensive load on each side to observe change in shape or deformity in the cylindrical panel with rectangular cutout. The above designed structure is tested under three different boundary conditions as shown in figure 5,6 and 7 it is observed from the simulations that the cylindrical panel can bear a maximum load of 0.15 N/mm because after applying external pressure a change in shape is observed at the outer structure and in the inner cut out rectangle which can be clearly observed in figure 9 and 10, the four different figures 9, 10, 11 and 12 shows four different points where the external pressure is applied and it is observed that maximum deformity occur when an external pressure is applied from the upper right corner of the designed cylinder.
9 Appendix
Table-1 Material Properties of unidirectional carbon/epoxy composites
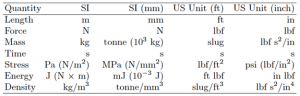
Table-2 Consistent sets of units