Japan’s Automakers Face Endaka Case Study Solution
What will they (Japanese automakers) have to do differently in 1995?
Although, the Super Endaka has the same implications as the 1985 Endaka, but this time the Japanese automakers should focus on previous measures along with certain new measures to avoid the effects of the Super Endaka over sales levels and the profit margins. As, they have created their strong foothold in the US markets with aggressive transplant of their production facilities during 1984 to 1995, now they should focus on more potential markets like Asia Pacific region. Moreover, in order to avoid the criticism in the local markets of declining production in Japanese plants and increasing unemployment, they should purchase certain future contracts to avoid the risk of loss from the exchange rate and to maintain a substantial amount of production level in the local markets. Along with it, the Japanese automakers should find out non served market segments in US and other global markets to increase their customer base and attain more revenue diversification.
What can a company do to protect themselves from changes of this kind?
A company, relying highly on exports for its revenue, could be highly affected by these kind of changes i.e. appreciation of local currency. However, there are certain measures that could be taken to protect the company from these type of changes. One of the major ways to protect against these type of changes is the currency hedging. For example, a Japanese company expected to export 500 units of its product to US market at a price of $2 after two months. The current exchange rate is ¥100 Yen per US dollar. It means, on the basis of current exchange rate, the company would receive $1000 or ¥100000 as revenue. However, if it expects the exchange rate to be ¥50 yen per US dollar. Now at the same price per unit, it would receive $1000 or ¥50000. However, the costs would remain the same if the company uses local inputs in manufacturing. In this way, the overall profits would reduce by ¥50000. This could impact the company highly. However, it could purchase certain future contracts to sell dollars at a predetermined rate i.e. ¥80 yen per US dollar to hedge the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. In this way, it would receive ¥80000 after two months as compare to ¥50000 without hedging.(Roberto J Santillán–Salgado, 2016)
What are the lessons from this case on operational ways to hedge demand and supply risks? How about hedging exchange rate risks?
With the analysis of the overall case and the strategies adopted by the Japanese automakers during the Endaka, which led them to survive in the US markets with an average positive sales growth, several operational ways could be concluded to hedge demand and supply risks. The first ever operational way is to diversify the production facilities. A company relying at one production facility could face a high risk of demand and supply problems as compare to one with diversified production facilities. Diversified production facilities allow you to manage the price levels, which is the main factor of demand and supply fluctuations in different regions. Moreover, diversification of the market segments is also one of the potential ways of hedging demand and supply risk. Diversification of market segments within a particular market and to a number of markets allows a company to reduce its reliance over on particular segment for its revenues. For example, a company targeting two different regions would face a low risk of demand fluctuation as compare to one relying on a single region. Along with the operational ways to hedge demand and supply risks, there is certain potential ways to hedge the exchange rate risks. One of the major ways for exchange rate risk hedging is to purchase certain future contracts. The implications of future contracts in hedging exchange rate risks is elaborated deeply in the previous section.
Conclusion
Even after the huge reliance of Japanese automakers over exports for their revenues, they were quite able to survive in the US markets despite of the two Endaka and the global recession 1993. The major reason of it was the critical strategies adopted by the Japanese automakers. However, the Super Endaka in 1995 is a little different and extreme from the first Endaka, therefore, the Japanese automakers must consider certain different strategies along with the previous measures to maintain their foothold in the US markets.
Appendices
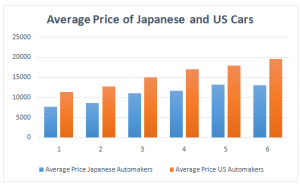
Appendix-1: Comparison of US and Japanese Car Prices
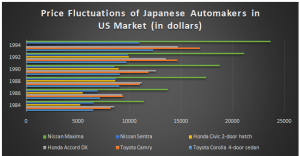
Appendix-2: Increase in Japanese Car Prices
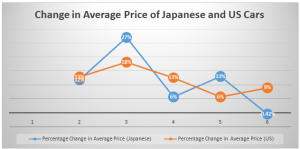
Appendix-3: Percentage Change in US and Japanese Car Prices
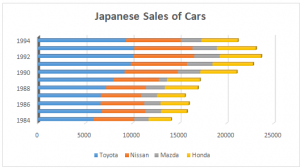
Appendix-4: Japanese Car Sales
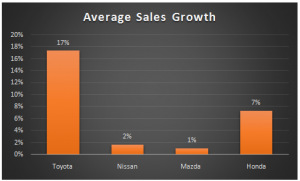
Appendix-5: Average Sales Growth
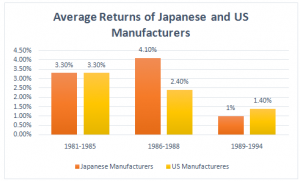
Appendix-6: Net Returns
This is just a sample partical work. Please place the order on the website to get your own originally done case solution.