INTRODUCTION TO MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Case Solution
QUESTION # O2
Profit and Output Maximizing behavior of Firms
1.Perfect Competition
Perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in which the following mentioned points are met.(HAYES, Perfect Competition, 2020) In perfect competition all firms sell same product, buyers have full information about the goods’ prices in which the product is being sold by every firm, share does not have any influence over price, all firms are price takers, firms can enter or exit the market without cost and capital for workers is completely mobile.
Rule for profit-maximizing perfectly competitive is to make the level of output,where:
Price= MR = MC
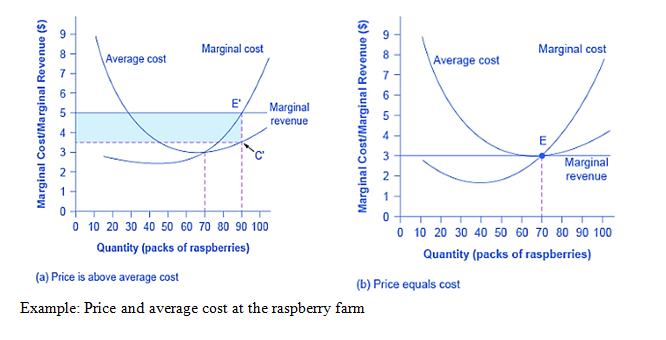
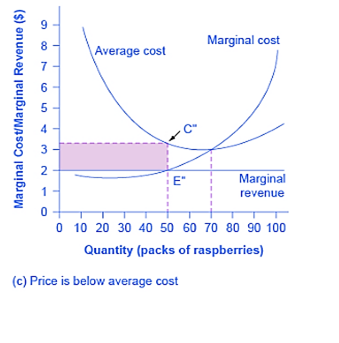
So the Raspberry farmer will make a quantity of 90 that are labeled as E in Figure ‘A,The area of a rectangle is equal to base multiplied by height.Profits will be the blue shaded rectangle on figure. (opentextbc)In figure ‘A’ Price intersects to the marginal cost (MC) above to the average cost (AC) curve because the price is more than the average cost-due to which the firm is making profit returns. In Figure ‘B’ price intersects to the marginal cost (MC) at the lower point of the average cost (AC) curve, because the price is equal to average cost, due to whichthe firm is in a break-even condition. In figure ‘C’, price intersects to the marginal cost (MC) curve below the average cost (AC) curve,where price is less than the average cost, due to which the firm is in losses.
1.Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is a market structure that takes the elements of monopoly and competitive markets. Monopolistic competitive markets have freedom of entry and exit, but organization are bringing differentiation in their goods. Monopolistic competitive markets have inelastic demand curve A monopolistic market has some highlighted qualities,such as: it has many firms, where every firm has the freedom of entry and exit, the firms are making differentiated goods, they are producing normal returns in long run but are making super normal returns in short term, firms are the price makers because their product is very strongly differentiated and the firms are productively inefficient. (STAFF, 2020).
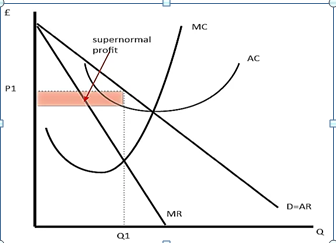
If the business is making an output at a point where marginal revenue (MR0 exceeds marginal cost (MC), then this business expands the production because each unit makes profit that increases the revenue of the firm. So, then the firms produce units at a point where MR = MC
Monopolistic competition and monopoly have same diagram in short run. The organization should maximize its returns where:
MR=MC
In this diagram at point (profit) Q1 and (price) P1, which leads to the supernormal profit
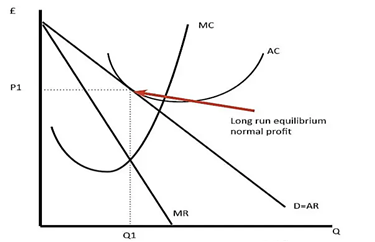
Monopolistic Competition for Long Run
New firms are entering in the market due to this the demand curve shifts to the left. New firms enter in the market because of the supernormal profit, due to which the demand of the existing firm decreases and leads towards a normal profit.
Example of Monopolistic Competition
Restaurants compete in the market on the basis of the price as well as the quality of food. Differentiation of product is an important element of the small or large businesses. There are low barriers for setting up a new food market or restaurant. Secondly a service that gives a reputation to firms or businesses because of the best quality of hair cutting.........................
INTRODUCTION TO MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Case Solution
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.