Financial decisions and valuation – Final Exam Case Studies
Introduction
The case refers the situation at Nisa Foods Corporation which is willing to acquire one of its competitor named Krad Foods. For the acquisition purpose the company has done the evaluation of Krad Foods by using various approaches such as DCF analysis and Market multiple approaches etc.
Situational Analysis
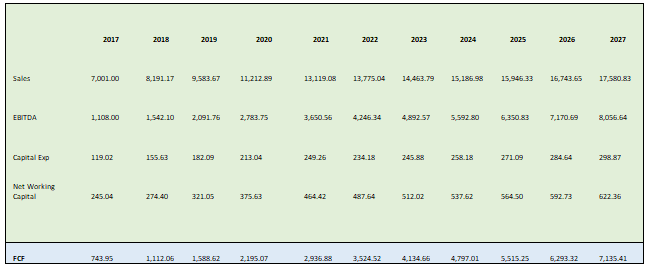
Free Cash Flow (FCF) projection (Question 1)
The FCF of the company are determined by using the formula as following.
FCF = EBITDA – change in working capital – Capital Expenditure
Since we have used EBITDA instead of EBIT so we have added the depreciation to the formula because it is already added to the EBITDA.
All the projections have been done by using the data given and the projected FCF are as follows.
DCF Analysis
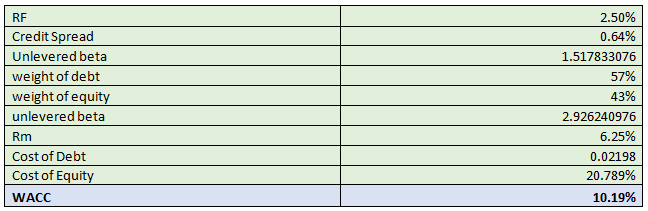
In order to do the DCF analysis of the company, first we determined the WACC by using the information given. The WACC is determined as under.
We determined the unlevered beta by dividing the comparable companies’ levered beta with 1+ (1-t)*debt/equity and then took its average. The average unlevered beta of comparable companies was then multiplied with 1+ (1-t)*debt/equity which is the basic formula to convert the value of unlevered beta to the levered beta by using its comparable companies’ data. After determining the beta we calculated the cost of debt b\y using the formula below.
(Risk free Rate (RF) + Credit Spread)(1-t)
To determine the cost of equity we have used the formula from Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) i.e.
Cost on Equity= RF+ Levered Beta * Risk premium
The WACC is determined as 10.19% by using the formula as below
WACC = (cost of equity)* (weight of equity)+ (cost of debt)*(weight of debt)
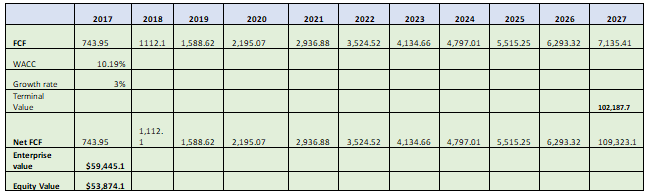
The DCF analysis of the company is done as following.
The terminal value of the company has been determined by using the perpetual growth rate of 3% and WACC as identified. The Enterprise value of the company has been identified as $59,445.08million dollars. The equity value of the company is identified by subtracting the company’s total debt for the 2017 from its enterprise value. By doing so the Enterprise value is calculated as $53,874.08million dollars.
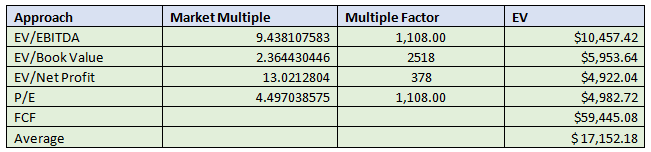
Evaluation using Market Multiples Approach (Question 4)
By using the market multiples approach the enterprise value has been determined as following
The leverage buyout (Question 5)
If the company decides to do leverage buyout than it will have to pay the percentage of participation to the venture capitalist in order to keep up with the process. That percentage of participation is determined as under.
In order to determine the rate of participation first we discounted back the initial investment of $20 million dollars at zero period by using the cost of capital at 20% that is the rate of return for the venture capitalist after five years. Then we determined the average of all calculated enterprise values using different approaches. Finally we divided the PV of initial investment with the average EV. By doing so the percentage of participation is calculated as 0.01%.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis different enterprise values have been determined by using different approaches. The highest enterprise value of the company have been determined by using the DCF analysis. It is because in the DCF analysis we have calculated the terminal value of the company as well. The average EV from all these approaches has been determined as $ 17,152.18 million dollars....
Financial decisions and valuation – Final Exam Case Studies
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.