ECON1101 Assignment Case Study Solution
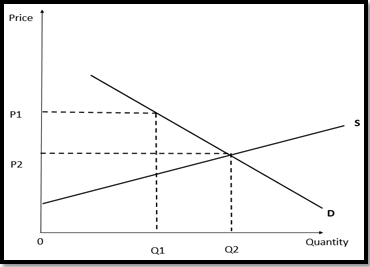
(A) Simple General Model of Demand & Supply
The demand and supply of unnatural food could be demonstrated using the basic principles of microeconomics. Consumers' preferences for convenience, taste, and affordability drive the demand for unhealthy fast food, while the production costs, such as the cost of ingredients, labor, and overhead, determine the supply of unhealthy ultra-processed food. As the price of this type of food declines, the capacity demanded upturns. Equally, when the value upsurges, the capacity demand declines. On the suppliers' side, when the price of unhealthy fast ood rises, the quantity supplied increases, while a lower price translates to a lower quantity supplied.
Given the lack of regulation in this market, it is not efficient due to the negative externalities of consuming unhealthy ultra-processed fast food. These external costs, such as increased healthcare costs, reduced productivity, and ill effects on quality of life, are not factored into the food's price, meaning consumers are not made to bear the full cost of their food decisions. In turn, the market fails to effectively and efficiently allocate resources. Moreover, there is a lack of information given to consumers, which may lead to an overconsumption of unnatural food. To conclude, an unfettered marketplace of unnatural food is not proficient as it does not consider the impacts of consuming these foods, and also fails to provide necessary information to its consumers.
(B) Implemented Taxes
Excessive consumption of unhealthy foods is known to cause health problems like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. This is a prime example of negative externalities, which refers to costs or benefits that aren't reflected in the market price of goods or services. To address this, taxes on unhealthy foods make economic sense as they help offset the external costs that arise from their consumption. On society as a whole, health problems can impose costs through the reduced quality of life, lost productivity, and increased healthcare costs.
Referencing the previous model constructed in part (a), it presents that implementing a tax on unhealthy food create various impact, which represents that the government implements a tax on unhealthy foods to correct market failures. This tax raises the price of unhealthy foods and thus reduces the quantity demanded by consumers. In this way, the negative externalities caused by overconsumption of unhealthy foods are addressed, which in turn encourages people to make wiser choices over the food they consume.
Such a tax's economic impact on efficiency relies on the circumstances of the unhealthy food market. Generally, an unhealthy food tax is expected to bring about a loss of economic efficiency known as a deadweight loss. This loss occurs when the tax leads to the consumption of fewer goods than in a free market. Unhealthy food taxes can lead to a loss of consumers due to a higher price, even though some will still consume the same amount as before.
(C) Improve Public Awareness
A successful public awareness campaign that encourages the benefits of a nutritionally balanced diet could lead to an alteration in consumer preferences towards a healthier range of foodstuffs. This alteration in demand would bring about a lesser equilibrium amount of unhealthy fast food being bought and a greater equilibrium price. From an economic standpoint, this shift in demand also has the potential to reduce deadweight loss and amplify total surplus in the market.
Public health goals often require more than just awareness campaigns. When it comes to managing individuals' considerable reliance on unhealthy fast food, for instance, imposing taxes may deliver better results than just offering information. Such a financial incentive encourages conscientious choices that do not rely on individuals voluntarily changing their behavior. Unhealthy fast food remains more convenient, accessible, and affordable than healthier alternatives, making it difficult to reduce consumption.
When it comes to deciding between a public awareness campaign and a taxation approach for improving public health, both have advantages and drawbacks. The taxation policy seeks to correct the imperfect information and externalities that may be hindering healthier food consumption, while the public awareness campaign encourages a shift in consumer attitudes towards healthier food options................
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.