Capitalism and the Party-State: The People’s Republic of China at 70 Case Study Analysis
Introduction
In the year 2019, the (70th) anniversary was celebrated by China (PRC). During this time, China has undergone tremendous changes, including the introduction of capitalism and the rise of the Party-State. In the year 1970 the economic reforms by “Deng Xiaoping” helped China become the wildest rising frugality in the globe, with a focus on export-oriented manufacturing and a vast labor force. This economic growth has been accompanied by the introduction of market-oriented policies, including the establishment of stock markets and the promotion of entrepreneurship and private enterprise.
At the same time, the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) has maintained tight control over political power in China. The Party-State has been responsible for implementing economic policies and regulations, while also maintaining a strong presence in areas such as education, media, and the military. In recent years, China has increasingly become a major player on the world stage, both economically and geopolitically. China seeks to increase its influence in (Asia, Africa, and Europe), while the military modernization program has seen significant investments in advanced weapons systems and expansion of its presence in the South China Sea.
Situational Analysis
“China's Accession” to the (WTO)
In 2001 December, China's accession to the WTO “World Trade Organization” was prefigured by the international communal that help to prove a victory over free trade and economic liberalization. The past 15 years present that it is very difficult for China but China made wide-ranging promises to restructure locally and improve efforts to reduce trade barriers. From the period of joining WTO by China, it becomes one of the establishment’s most active members and from that time the economy of China has become an essential relation in worldwide supply chains.
During the process of accession of China with WTO, the WTO members need Beijing to create important restructuring commitments that ultimately help to decrease government interference under national frugality. These promises need to include various accession protocols, which include reducing tariff rates, reducing trade barriers, and prices set by markets, removing subsidies on exports, and applying restructurings to increase accountability.
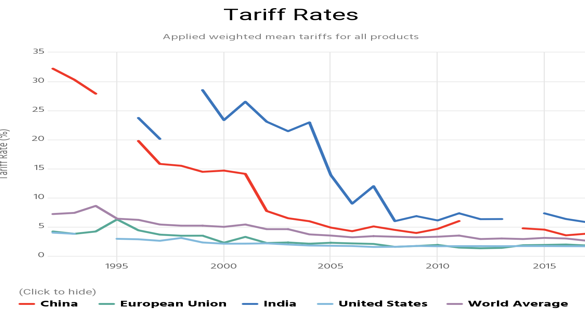
After the accession of WTO, China became its (143rd) member and it experience volatile growth in trading. By reducing the tariff rates by China the trades become good and moved from ($516.4 billion) to ($4.1 trillion) in the year 2001 to 2017 respectively. The average weighted tariff of China in the year 1992 is about 32.2%, which is considered to be very high compared to the world average of about 7.2%. Now in the year 2002, China reduces its tariff rates and it becomes 7.7%. The data also presents that the tariff rate for China is 4.8% on average between the years 2003 and 2017.
Performance of China after Accession
China's accession to the “World Trade Organization” clear a significant turning point in its economic development. Since then, China partakes proficient and significant financial progress and has turned into the globally “second-leading” frugality. Here are some of the key ways in which China has performed since joining the WTO, which include economic growth, trade expansion, foreign investment, and structural reforms.
This accession helped to facilitate its addition to the global economy, which has been a major driver of its rapid economic growth. Since joining the WTO, the GDP of China has grown up at a usual yearly ratio of around 10%, creating one of the wildest-rising major frugality in the world. China's trade has expanded rapidly since joining the WTO, as the country has become an increasingly important player in the global trading system. In the year 2019, it becomes the globally leading retail exporter and second-leading trader, accounting for around 13% of global trade.
China has become an increasingly attractive destination for foreign investment since joining the WTO. According to the (UN) Session on Trade and Enlargement, China was the second-leading beneficiary of “foreign direct investment” (FDI) in the globe in the year 2020, with inflows of $149 billion. To comply with WTO rules, China has undertaken significant structural reforms to its economy, including reducing tariffs, improving intellectual property rights protection, and opening up its services sector to foreign competition................
Capitalism and the Party-State The People’s Republic of China at 70 Case Study Analysis
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.