The Dee Beers Group: Exploring the Diamond Reselling Opportunity Case Study Solution
Business level strategy of De Beers includes its plan to provide high value to the diamond sellers to get competitive advantage.
The company sells rough diamonds as well as resell the used diamonds. The company deals in both the upstream as well as in the downstream area of the diamond industry. It describes the corporate level strategy of De Beers to gain competitive advantage.
The company has a strategic alliance with the Anglo American Group of companies owning its 85% of share as well an international alliance with Botswana owning 15%of the company. The strategies move with our analysis to give company a competitive advantage.
Firms main problem include the opening of a new dimension in the current business, introduction of new systems to manage the reselling business, management of demand levels for recycled diamonds, capital requirement, managing the aggressiveness of its stakeholders etc.
De Beers should manage demand for recycled diamonds by making itself efficient in recycling to reduce recycling cost. It should try to increase the demand of diamonds at whole to compensate the aggressiveness of its stakeholders to fulfil its capital requirement i.e. wholesalers, by improving selling experience of diamond purchasers.
The most important 7 S of implementation includes systems, strategy and structure, as system and structure need to be changed due to change in the business dimension, and the four strategies stated above have to be implemented. (Robert H. Waterman, 1980)
Questions for class discussions are:
What are the Risks and benefits of the Reselling Diamond market? Do the benefits exceed the risks? How How De Beers would manage its market share in the Reselling Diamond Business, if its close competitors at international would enter in the market?
Exhibits
Exhibit A: Porters Five Forces Model
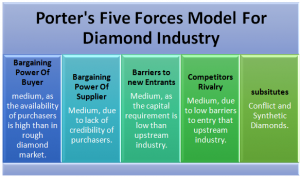
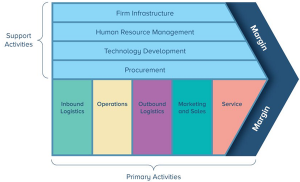
Exhibit B: Porter’s Value Chain Model
Exhibit C: Comparison of De Beers Group and Industry Ratios
| Ratio | De Beers | Upstream Industry |
| Profitability (Revenue 2014) | $7114 millions | $15 billions |
| Profitability (Operating Margin 2014) | 19% | 12.5% (on average basis) |
| Debt to total capital Ratio (taken by Anglo American Financial Statements 2014) | 37% | N/A |
| Price per carat | $198 | $200 |
| Cost per carat | $111 | $120 |
| Number of carats sold in millions | 32.73 | 70 |
| Market share 2014 (32.73/70) | 46.75% | N/A |
Exhibit D: VRIO Analysis
| Criteria | High Value To Supplier |
| Value | De Beers seems quite capable of exploiting the opportunity of increasing profit margins and demand for diamonds, as it provide a possible price, much closer to the wholesale price to diamond sellers. |
| Rarity | Most of the purchaser of used diamonds do not provide high value to the sellers, as they are unable to detect the quality of the diamond provided, thus charge a high price. |
| Imitability | Competitors like Pawn Shops, individuals etc. have less capability of providing high price to the diamond seller, as they have lack of trust worthiness among each other. |
| Organization | The firm is quite able to explore the opportunity, as it has tried it in its pilot program and got favourable results from it. |